Introduction
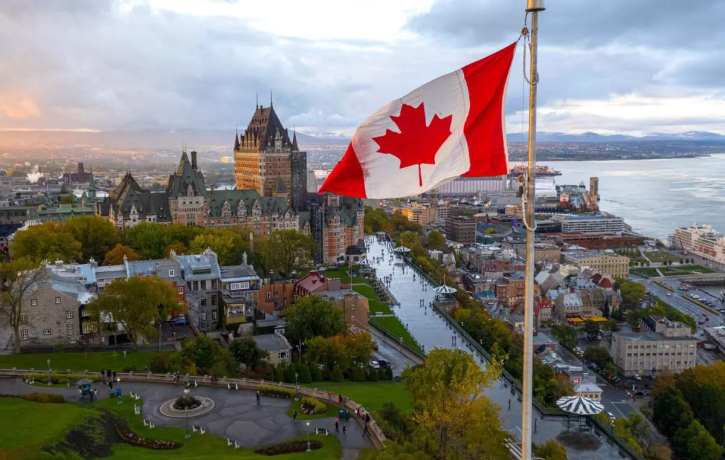
Canada, Across the Atlantic, Pacific, and Arctic, is the second-largest country in the world by land area. Ottawa, the nation’s capital, is home to more than 41 million people, the majority of whom live in urban areas like Vancouver, Toronto, and Montreal. Although there have been indigenous peoples for thousands of years, Canada only gained full independence from the UK in 1982. It was established as a federal dominion in 1867. Recognized for its strong economy, varied population, and excellent standard of living, it is a constitutional monarchy and multilingual parliamentary democracy. In addition to supporting multilateralism, Canada participates actively in international organizations.
Etymology
The word “Canada” comes from the St. Lawrence Iroquoian word “kanata,” which means “village” or “settlement.” Native Americans used it to direct French adventurer Jacques Cartier to the Stadacona town in 1535. Later, Cartier adopted the term “Canada” to refer to the surrounding area, and by 1545, it was marked on maps of Europe. Originally, the term “Canada” applied to the region of New France west of the Saint Lawrence River. It identified the two British colonies of Upper and Lower Canada by 1791. These two colonies merged to form the British Province of Canada in 1841. By the 1950s, “Dominion of Canada” had been superseded by “Canada” as the official name following Confederation in 1867. The national holiday was renamed Canada Day in 1982 after the name was officially adopted by the Canada Act of that year.
Geography
Canada is the fourth-largest country in the world by land area alone and the second-largest by overall area, including its seas. It stretches from the Atlantic to the Pacific and Arctic Oceans across 9,984,670 km² (3,855,100 sq mi). At 243,042 km (151,019 mi), it has the longest coastline. Its land border with the United States is the longest, while its marine borders are with Greenland and the French islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon. The northernmost settlement in Canada is called Alert, and it is located on Ellesmere Island, 817 kilometers from the North Pole. Seven physiographic zones, vast boreal forests, a substantial amount of ice cover, fruitful plains. more than two million lakes holding a large portion of the world’s fresh water are all part of its varied geography. There could be volcanoes and earthquakes in this active geological region.
Climate
Canada has a wide range of temperatures: warmer winters are experienced in coastal British Columbia, while harsh winters are experienced in the interior and Prairies, with lows often around −15°C (5°F) and occasionally below −40°C (−40°F). Summertime highs can be found inland at over 40°C (104°F) and by the coast at low 20s°C (70°F). Rapid Arctic warming threatens the ice and permafrost in Northern Canada. The average temperature has climbed by 1.7°C (3.1°F) since 1948, with the North and Prairies experiencing the greatest increases. Acid rain is a result of air pollution, which has an adverse effect on the environment. Between 1990 and 2022, Canada’s greenhouse gas emissions increased by 16.5%.
Biodiversity
More than 80,000 different wildlife species can be found in Canada’s 15 terrestrial and 5 marine ecozones, and there are still many more to be found. There are just about 800 endemic species, but they are all in danger. Approximately 65% of species are classified as “Secure,” and over half of Canada’s territory is still unspoiled. With a land area of almost 3,000,000 km², the boreal forest is the largest unbroken forest in the world (1,200,000 sq mi). 13.8% of territorial waters and 12.1% of land and freshwater are protected. The Scott Islands Marine National Wildlife Area, Lake Superior National Marine Conservation Area, Algonquin Provincial Park, and Banff National Park are a few notable protected places.
Health
The Canada Health Act of 1984 established Medicare, the country’s universal, publicly funded healthcare program. Private insurance pays for about 30% of healthcare expenses, mostly for dentistry and prescription medication needs. Most Canadians, between 65 and 75 percent, have additional insurance, frequently via their jobs. An aging population and rising healthcare expenditures resulted in $308 billion, or 12.7% of GDP, being spent on healthcare in Canada in 2021. Even though Canada’s health statistics are usually good, there are still issues with long wait times, chronic illnesses, high infant mortality, and a lack of medical personnel.
Education
In Canada, the federal, provincial, and local governments are principally responsible for funding and supervising education. Primary, secondary, and post-secondary levels are covered, and both French and English are the languages of instruction. Canada is home to numerous publicly financed universities, the biggest of which is the University of Toronto. As on OECD 2022, Canada holds the top position in terms of the proportion of adults with post-secondary education, allocates 5.3% of its GDP towards education, and has an adult literacy rate of 99%. With average student scores above the OECD norm, the nation excels in reading, math, and science.