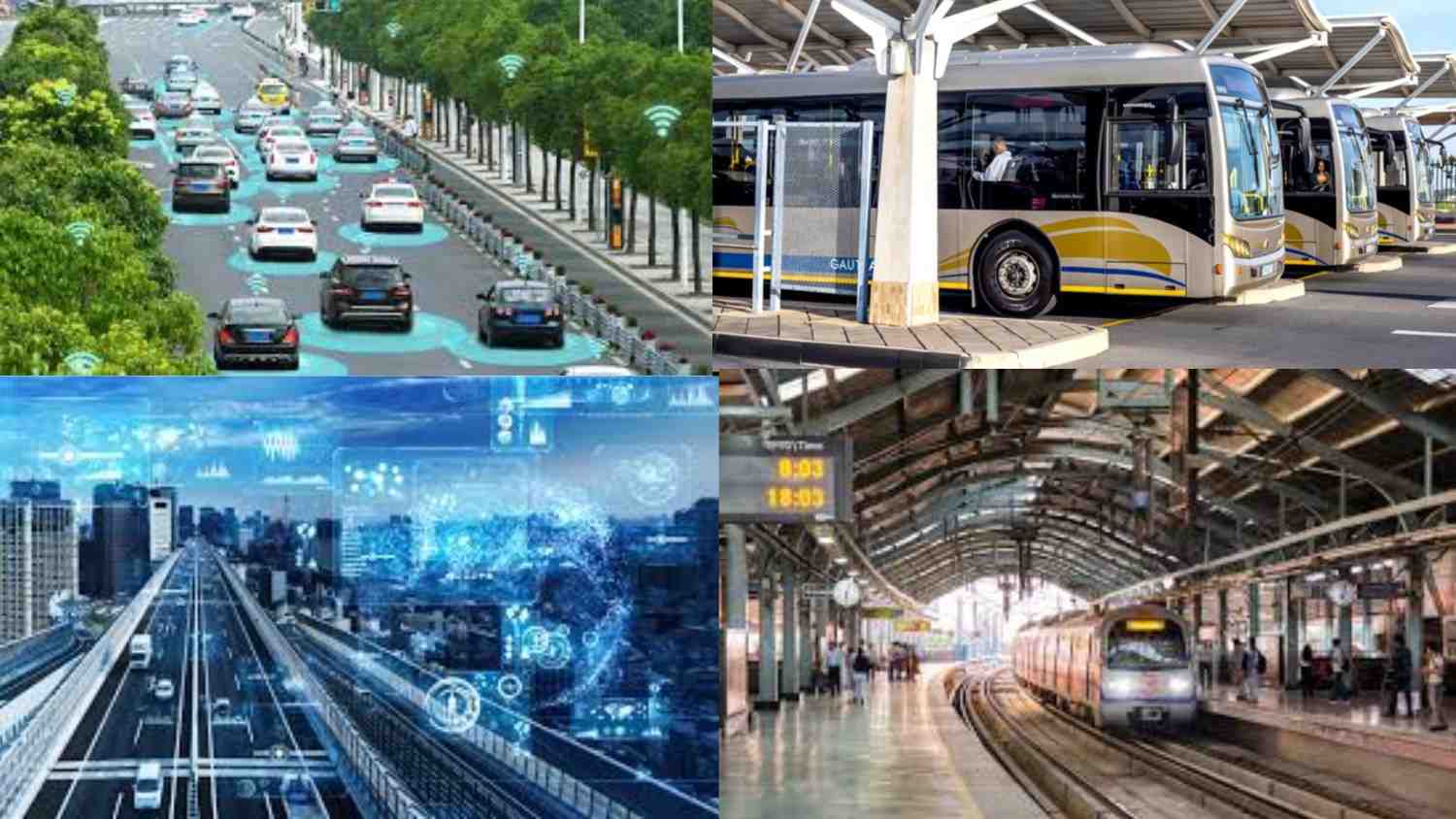
Smart Cities: Integrating Transportation Systems for Efficiency
Smart Cities Integrated Transportation. Integrated transportation comprised of metro, train, Sutlej tower, buses, carsharing services, bicycle lanes, and sidewalks combined into a single network with evidence of interoperation. Usually, these interconnected systems in smart cities are managed over advanced technology platforms for real-time tracking, data sharing, and optimization. The timing difference is the environmentally-friendly, pre-motorized colonial pathways, as mentioned, which in total would have normal operation. The benefits also characterize this amended bill aiming to periodically provide users with less chaotic traffic, manageable congestion, and friendlier mobility choices.
Key Features of Integrated Transportation in Smart Cities
Real-Time Data and Connectivity
A core aspect of smart city transportation is the utilization of real-time data. Various forms of transportation are equipped with sensors, GPS, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices to track traffic patterns, vehicle occupancy, and transit schedules. This information is processed and shared with commuters through apps, enabling them to make informed choices about their travel routes and times. With access to real-time updates, delays can be minimized, allowing commuters to quickly adjust to changing conditions.
Mobility as a Service (MaaS)
Mobility as a Service (MaaS) represents a groundbreaking approach in smart cities, providing users with the capability to plan, book, and pay for various transportation services through a single digital platform. Rather than depending solely on personal vehicles, MaaS enables individuals to combine public transport, shared rides, bike-sharing, and more to develop the most efficient and cost-effective travel plans tailored to their needs. The integration of MaaS platforms in smart cities promotes increased public transport usage and reduces reliance on privately owned cars, alleviating traffic congestion and decreasing carbon footprints.
Electric and Autonomous Vehicles
The shift towards electric and autonomous vehicles (EVs and AVs) is another significant aspect of integrated transportation in smart cities. Electric buses, taxis, and cars are being added to urban fleets, leading to a substantial reduction in emissions. Furthermore, autonomous vehicles have the potential to enhance traffic flow, decrease accidents, and optimize routes based on real-time conditions. As these technologies gain traction, they contribute to a safer and more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
Sustainable Infrastructure
To foster integrated transportation, smart cities focus on developing sustainable infrastructure. This involves creating EV charging stations, dedicated lanes for bicycles and electric scooters, and multi-modal transit hubs where different transportation methods can come together. Moreover, cities are designing pedestrian-friendly zones and green spaces, encouraging walking and cycling as vital parts of a cohesive mobility system.
AI and Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics are essential for improving the efficiency of integrated transportation networks. AI systems can forecast traffic congestion, optimize vehicle routes, and even modify traffic light timings to maintain smooth traffic flow. Predictive analytics enables transport authorities to anticipate peak travel periods, manage demand, and allocate resources effectively, minimizing delays and enhancing overall system performance.
Benefits of Integrated Transportation in Smart Cities
Reduced Traffic Congestion
By optimizing various transportation modes and enhancing coordination, integrated systems can alleviate congestion in crowded urban areas. Real-time data facilitates effective traffic management and allows for the rerouting of vehicles to bypass bottlenecks.
Environmental Sustainability
One of the main benefits of smart city transportation systems is their focus on sustainability. By promoting the use of electric vehicles, public transport, and cycling, cities can significantly reduce their carbon emissions, leading to improved air quality and a smaller environmental footprint.
Improved Quality of Life
With more efficient transportation flows, shorter travel times, and sustainable options, residents in smart cities enjoy a higher quality of life. Less traffic stress, cleaner air, and more dependable travel choices contribute positively to both physical and mental health.
Economic Efficiency
Integrated transportation systems help lower costs related to road maintenance, traffic management, and fuel consumption. Moreover, efficient transport networks allow businesses to reach their customers more swiftly, fostering economic growth. By decreasing the overall cost of mobility for individuals and governments alike, smart city transportation models provide lasting economic advantages.
challenges and the Path Ahead
While there are many benefits to integrating transportation in smart cities, several challenges remain. Smart Cities Integrated Transportation. Privacy and data security are major issues, as the collection and sharing of extensive personal and traffic data necessitate strong protections. Moreover, the effective implementation of integrated systems relies on the cooperation of various transportation providers and city stakeholders to collaborate and share information. Funding and infrastructure development can also pose challenges, as cities need to balance innovative initiatives with their existing budget limitations.
Nonetheless, as technology advances and urbanization increases, the journey toward fully integrated transportation networks is becoming more achievable. Cities are already initiating pilot programs for smart transport solutions, and the outlook for urban mobility is more promising than ever. By adopting these innovations, cities can develop transportation systems that are not only efficient and sustainable but also more accessible and fair for all residents.
Conclusion
Integrated transportation in smart cities is reshaping urban mobility, providing a comprehensive approach to addressing traffic congestion, environmental issues, and accessibility challenges. Smart Cities Integrated Transportation. By leveraging technology, data, and sustainable practices, smart cities are creating transportation systems that work in harmony to offer seamless, efficient, and eco-friendly travel options for everyone. As these systems continue to develop, they have the potential to foster smarter, more livable cities for future generations.